River Walk Dental Orthodontics
Blog
Dental hygiene tips for healthy teeth & gums
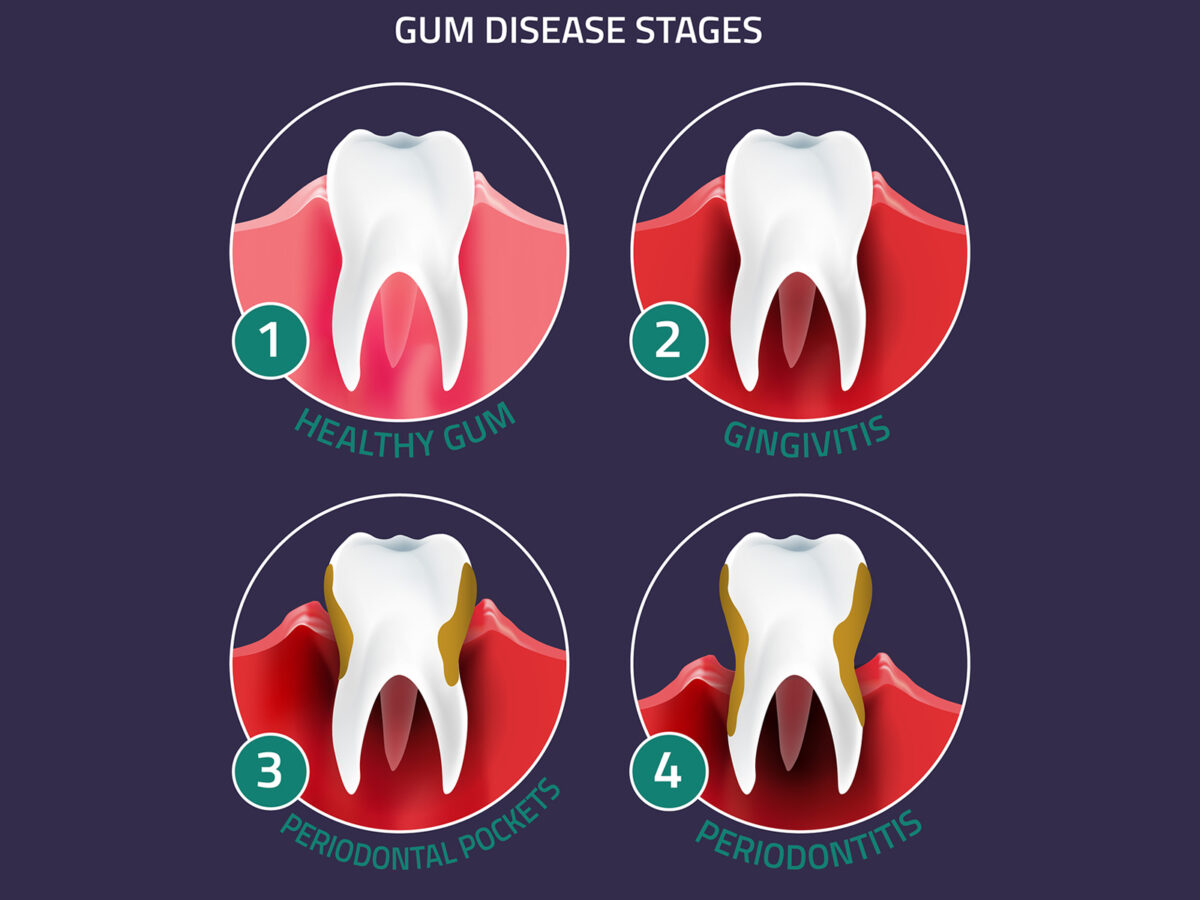
Understanding The Stages of Gum Disease
When you think of gum disease, you might envision a singular condition with a specific set of symptoms. However, gum disease encompasses a range of conditions affecting the tissue surrounding your teeth. Both younger and older individuals can be affected. If you suspect you have gum disease, understanding its stages is crucial.
The stages of gum disease are distinct, with varying treatment and management options. The prognosis for each stage largely depends on its progression. In this blog, you’ll delve into the different stages of periodontal diseases and their associated signs and symptoms.
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, often referred to as periodontal disease, is a dental condition affecting the gums surrounding teeth, leading to inflammation and infections. It primarily results from bacteria in the mouth. If unchecked, bacterial growth can harden into plaque and tartar. This hardened plaque can be acidic, causing the protective gum tissue and bones to deteriorate over time.
Bleeding
One of the earliest indicators of gum disease is bleeding during brushing or flossing. This might manifest as a pink spot on your toothbrush or post-floss bleeding. If you notice this, consult your dentist, as it could be an early sign of underlying gum disease.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the initial stage of gum disease, potentially causing swollen and painful gums. Gums might bleed or exude pus due to plaque accumulation along the gumline. With diligent dental care, your dentist can remove plaque, potentially halting or even reversing the progression of gum disease.
Early Periodontitis
The third stage of gum disease is termed early periodontitis. During this phase, individuals might experience sore and swollen gums. Plaque solidifies into tartar, indicating decay. If neglected, gum disease can begin to harm the underlying jawbone.
Moderate Periodontitis
Moderate periodontitis, the fourth stage of gum disease, manifests as receding, sore gums. Teeth become more prone to injury, decaying rapidly. Teeth might become loose, and the jawbone can become significantly infected. If you’re at this stage, you might also detect a foul-tasting discharge from inflamed gums. This condition is severe and necessitates an urgent dental consultation.
Advanced Periodontitis
The final stage, advanced periodontitis, can result in tooth loss without prompt dental intervention. The infection compromises the jawbone, potentially leading to tooth loss. Chronic pain is a common symptom of advanced periodontitis.
Treatment
Early detection and treatment with antibiotics and thorough cleaning can effectively combat gum disease. However, prolonged neglect makes gum disease harder to treat and reverse. In extreme cases, surgery might be necessary to eradicate infection.
Regular dental check-ups are pivotal for early gum disease detection, facilitating effective treatment and reversing potential damage. Early stages like gingivitis are common in adults over 30 and can be managed with oral care, including regular dental cleanings, brushing, flossing, and using fluoride mouthwash. Routine dental visits are crucial for detecting periodontal disease in its infancy and securing appropriate treatment to prevent its progression.
